Structural Isomers Definition
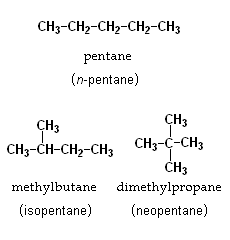
Structural isomerism, or constitutional isomerism, is a type of isomerism where isomers have same molecular formula but have different arrangements of atoms within the molecule. e.g. n-pentane, isopentane and neopentane are structural isomers.
Types of isomerism
Structural isomerism is of five types:
- Chain isomerism
- Position isomerism
- Functional group isomerism
- Metamerism
- Tautomerism
1. Chain isomerism
Chain isomerism is a type of structural isomerism where the isomers have same molecular formula but they differ in the order in which the carbon atoms are bonded to each other. Thus the isomers arise with different types of branching in carbon chains. For example, Pentane, C5H12, has three chain isomers. These are n-pentane, isopentane and neopentane.

2. Position isomerism
Position isomerism is a type of structural isomerism where the main carbon skeleton are same but they differ in the position of functional group attached to it. For example, there are two structural isomers occurs in n-butanol with the molecular formula C4H9OH. In one of them the functional group -OH is on the end of the chain, whereas in the other it is attached to the second carbon of the main carbon chain.
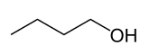
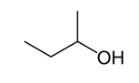
Butan-1-ol Butan-2-ol
3. Functional group isomerism
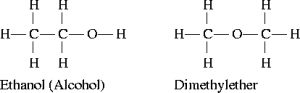
Functional group isomerism is a type of structural isomerism where isomers have same molecular formula but differ in functional group. Thus they belong to different families of compounds or different homologous series. For example, there are two functional group isomers found with the molecular formula C2H6O. Ethanol and dimethyl ether are those two functional group isomers. Here ethanol contains alcohol as functional group and dimethyl ether contains ether.
Metamerism
Metamerism is a type of structural isomerism where the isomers have same molecular formula but differ due to the different number of carbon atoms or alkyl groups on either side of functional group ( i.e., -O-,-S-, -NH-, -C(=O)-). The isomers belong to the same homologous series. For example diethyl ether and methyl propyl ether are two metamer wit the same molecular formula C4H10O. Here diethyl ether has ethyl group on both side of oxygen whereas methyl propyl ether has methyl on one side and propyl on another side of oxygen.
![]()
Diethyl ether methyl propyl ether
Tautomerism
Tautomerism is a special type of structural isomerism where the isomers stays in dynamic equilibrium with each other by simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion. Tautomers only differ in the position of the protons and electrons within the molecule while the carbon skeleton of the compound remains unchanged. For example 2-butanone (keto-form) and 2-butanol (enol-form) stays in dynamic equilibrium by transferring a hydrogen atom from number 3-carbon to oxygen. This dynamic equilibrium reaction is also known as keto-enol tautomerism. The molecular formula of these tautomers are same that is C4H8O.
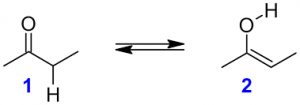
2-butanone 2-butanol
Keto-form Enol-form
Summary
- Structural isomerism is a type of isomerism where isomers have different arrangements of atoms within the molecule.
- Chain isomerism where the isomers differ in the order in which the carbon atoms are bonded to each other.
- Position isomerism where the main carbon skeleton are same but they differ in the position of functional group attached to it.
- Functional group isomerism where isomers differ in functional group.
- Metamerism where the isomers differ due to the different number of carbon atoms or alkyl groups on either side of functional group.
- Tautomerism where the isomers stays in dynamic equilibrium with each other by simple proton transfer.