Covalent Bond Definition
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms. These electron pairs are known as bonding electron pairs, and they share these electrons to form covalent bond. This bonding is primarily found between nonmetals; however, it can also be observed between nonmetals and metals.
Covalent Bond Example
A most common compound methane contains covalent bond where four hydrogen’s covalently bonded with one carbon center.
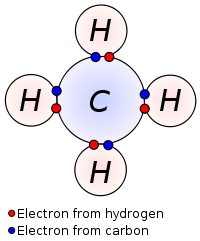
Carbon has four valence electrons, half of an octet. To make ionic compound it needs to loss or gain 4 electrons. Both are unfavorable, thus it shares 4 electrons with 4 hydrogens. Each hydrogens are also satisfied by sharing their electrons with carbon.
Types of covalent bond
A. Depending on the number of shared electron pair or the bond occurs between two atoms, covalent bonds can be classified in 3 different types.
- Single covalent bond
- Double covalent bond
- Triple covalent bond
B. Depending on polarity covalent bond is classified in 2 different types:
- Non polar covalent bond
- Polar covalent bond
A. Depending on the number of shared electron pair
1. Single covalent bond
When a covalent bond is formed by sharing one pair of electron by two atoms then it is called single covalent bond. Single covalent bond is formed by head to head overlapping of two orbitals of two atoms. This way a sigma bond is formed which is stronger compare to other two covalents bonds. Single covalent bond is denoted by single short line (-). e.g. H-Cl.
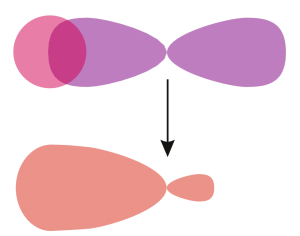
Here a sigma bond is formed by head to head overlapping of one s and one p orbitals.
2. Double covalent bond
When two covalent bonds are formed by sharing two electron pairs between two atoms then it is called double covalent bond. In double covalent bond, one is a sigma bond formed by head to head overlapping of two orbitals of two atoms, and other one is a pi- bond formed by side to side overlapping of two orbitals of two atoms. It is denoted by two short lines (=). e.g. CH2=CH2
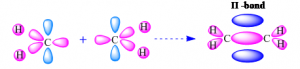
3. Triple covalent bond
When three covalent bonds are formed by sharing 3 electron pairs between two atoms then it is called triple covalent bond. In this type of bond, one is sigma and other two is pi- bond formed by side to side overlapping. It is denoted by three short lines (≡). e.g. CH≡CH
B. Depending on polarity
1. Non polar covalent bond
A non polar covalent bond is formed when two same atoms share electrons by head to head overlapping (single covalent bond). As this bond is formed between two same atoms the difference in electronegativity is zero thus they both attract bonding electron pair equally and no polarity is found within the molecule. e.g. H2, N2, O2 etc.
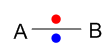
Here 2 equal electronegative atoms A and B are sharing their bonding electron pair equally to form non polar covalent bond.
2. Polar Covalent bond
A polar covalent bond is formed when different electronegative non metallic atom shares their bonding electron pair between themselves. Here a polar sigma covalent bond is formed by head to head overlapping. Because of different electronegativities, the atoms share bonding electron pair unequally and the bonding electron pair tends to stay closer to the more electronegative atom. e.g. H-Cl, H-F etc.
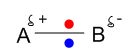
Here two different electronegative atoms are sharing their bonding electron pair unequally to form polar covalent bond. If we assume B as a more electronegative atom, the bonding electron pair will be attracted more by this element and a partial negative charge (δ-) will be developed on this element. On the other hand A will have partially positive charge(δ+) as a result of its less electronegativities.
Summary
- Covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by sharing electron pairs between two atoms.
- Covalent bond can be single, double or triple bond depending on the number of bonding pairs of ele