Oxidation Reduction Reaction Definition
An oxidation-reduction (redox) is a chemical reaction involving transfer of electrons between two species. An oxidation-reduction reaction is any chemical reaction where the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion changes – by gaining or losing an electron. The redox reactions are very common and vital to the basic functions life, using in processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, and corrosion or rusting.
Oxidation reduction reaction can be explained in four different ways:
- In terms of electron transfer
- In terms of oxygen transfer
- In terms of hydrogen transfer
- In terms of oxidation number
Redox Reaction Examples
Electron Transfer
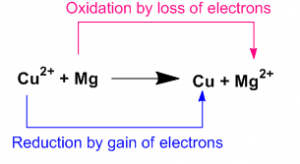
- Oxidation is the loss of electrons.
- Reduction is the gain of electrons.
The following equation shows a very simple redox reaction which can be explained in terms of electron transfer.

Cupper (II) oxide and Magnesium oxide are ionic whereas Cupper and Magnesium are metal (not ionic). By leaving out the Oxide ions as spectator ions we can rewrite the equation as:
Oxidizing and Reducing Agent
- Oxidizing agent is the agent which oxidizes other substance.
- Reducing agent is the agent that reduces other substance.
Oxidizing agent gains electron during the reaction. In above reaction Cupper ion is the oxidizing agent as it gains 2 electrons to form Cupper.
Reducing agent losses electrons during the reaction. In above reaction Magnesium is the reducing agent as it losses 2 electrons to form Magnesium ion.
Oxygen transfer
- Oxidation is the gain of oxygen.
- Reduction is the loss of oxygen.
The same redox reaction can also be explained in terms of oxygen transfer.
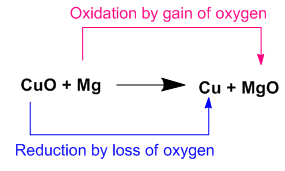
Here Cupper (II) oxide loses oxygen to form Cupper and Magnesium gains oxygen to form Magnesium oxide.
Oxidizing and Reducing Agent
Oxidizing agent loses oxygen during the reaction. Here Cupper(II) oxide loses oxygen to form Cupper. Thus it is an oxidizing agent.
Reducing agent gains oxygen during the reaction. Here Magnesium gains oxygen to form Magnesium oxide. Thus it is an reducing agent.
Hydrogen transfer
- Oxidation is the loss of hydrogen.
- Reduction is the gain of hydrogen.
The redox reaction between ammonia and bromine to form nitrogen and hydrogen bromide.

Here ammonia loses hydrogen. Ammonia is oxidized to become nitrogen. Thus this is an oxidation process. On other hand bromine gains hydrogen or bromine reduced to become hydrogen bromide. Thus this is a reduction process.
Oxidizing and Reducing Agent
Oxidizing agent gains hydrogen during the reaction. Here bromine is an oxidizing agent as it gains hydrogen to form hydrogen bromide.
Reducing agent loses hydrogen during the reaction. Here ammonia loses hydrogen to form nitrogen. Thus ammonia is a reducing agent.
Oxidation number
- Oxidation involves an increase of oxidation number.
- Reduction involves a decrease of oxidation number.
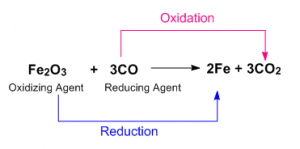
Oxidation number of an atom is the charge that atom would have if the compound would have composed of ions. e.g. the oxidation number of Fe and O in Fe2O3 is 3 and 2 respectively as it is composed of 2Fe3- and 3O2-.
The oxidation number of an atom is zero in a neutral substance that contains atoms of only one element. e.g. the oxidation number of atoms in N2 is 0.
By taking one of the above redox reactions oxidation reduction reaction can be explained in terms of changing oxidation number.
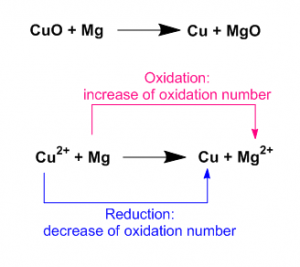
Here the oxidation number of Magnesium increases from 0 to +2. So this is an oxidation process. On other hand Cupper(II) ion reduced to Cupper. The oxidation number decreases from +2 to 0.
Oxidizing and Reducing Agent
The oxidation number of oxidizing agent decreases during the reaction. Here Cupper (II) ion is an oxidizing agent as the oxidation number of Cupper(II) ion decreases from +2 to 0.
The oxidation number of reducing agent increases during the reaction. Here Magnesium is a reducing agent as the oxidation number of magnesium increases from 0 to +2.
Summary
Oxidation is:
- the loss of electrons.
- the gain of oxygen.
- the loss of hydrogen.
- the increase of oxidation number.
Reducing agent helps to oxidize other substance. Reducing agent:
- loses electrons.
- gains oxygen.
- loses hydrogen.
- increases oxidation number.
Reduction is:
- the gain of electrons.
- the loss of oxygen.
- the gain of hydrogen.
- the decrease of oxidation number.
Oxidizing agent helps to reduce other substance. Oxidizing agent:
- gains electrons.
- loses oxygen.
- gains hydrogen.
- decreases oxidation number.