Hydrogen Bond Definition
Hydrogen bond is an attractive force between a partially positive charged hydrogen and a partially negative charged atom (oxygen and nitrogen). This is a very weak bond and strength of hydrogen bond (5-10 Kcal per bond) is much less than the strength of covalent bond. Hydrogen bonds are usually showed as dotted lines between two atoms. For example hydrogen bond between two molecules of water is shown below:
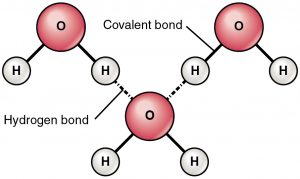
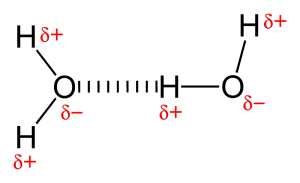
Reason of hydrogen bonding
Because of the presence of very electronegative atom like oxygen or nitrogen, the shared electron pair between oxygen and hydrogen are pulled towards the more electronegative atom. This unequal distribution of electron pair leads to the formation of two partial dipole. The partially positive charged hydrogen is then attracted by the other partially negative charged oxygen or nitrogen is known as hydrogen bond.
Types of hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding can occur between two atoms of same molecule or between two atoms of different molecule. Depending on that hydrogen bonding are of two types:
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding
- Intramolecular hydrogen bonding
1. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding
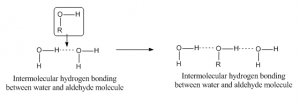
When hydrogen bonding occurs between to atoms of different molecule then it is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding. For such bonding one molecule should have a partially positive hydrogen as acceptor atom and another should have a partially negative or donor atom. As for example, hydrogen bonding between aldehyde and water molecule has given below:
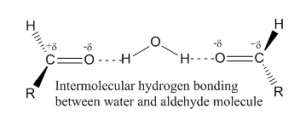 2. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding
2. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding
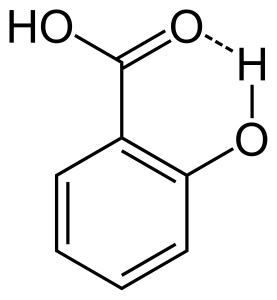
When hydrogen bonding occurs between two partially charged atoms of same molecule that is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding. This occurs when two functional groups are present in same molecule and they are in such way that can attract each other to form hydrogen bond. For example salicylic acid has two functional groups alcohol and carboxylic acid. Here intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between the hydrogen atom of alcohol group and the oxygen atom of carboxylic acid group.
Effects of hydrogen bonding
On boiling point
It is expected that the boiling point of substances with same or similar molecular weight should have same or similar boiling point. The boiling point of ether and alkane of similar molecular weight are not far apart. But the boiling point of alcohols is much higher than ether of similar molecular weight. This can be explained in terms of hydrogen bonds. Because of hydrogen bonding in alcohol the boiling point rises up. Extra energy is needed to break the hydrogen bond before it boils. As there are no hydrogen bonds alkane and ether have low boiling point.

On solubility
Alcohols are soluble in water but alkanes are not. This is because, intermolecular hydrogen bonded compounds can dissolve in intermolecular hydrogen bonded solvent. A polar molecule like alcohol can enter into two water molecule to form hydrogen bond, while a non polar substance like alkanes can not. However with the increase of carbon chain in alcohols the solubility decreases as the long chain get in the way to form hydrogen bond.
Summary
- Hydrogen bond is an attractive force between a partially positive charged hydrogen and a partially negative charged atom.
- When hydrogen bonding occurs between to atoms of different molecule then it is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
- When hydrogen bonding occurs between two partially charged atoms of same molecule that is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Because of intermolecular hydrogen bonding the boiling point of polar compounds are higher than no polar compounds with same a.
- Because of hydrogen bonding between organic compound and water, the solubility is possible to some extent.