Electronegativity Definition
Electronegativity is a chemical property that measures the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. Electronegativity is affected by the atomic number and the distance between the valence electrons and its nucleus. The higher the electronegativity is the more it attracts the electrons towards it.
Types of Electronegativity
Non Polar Bond
When two atoms with equal electronegativity are bonded together in a molecule, a non polar bond is formed. These two atoms attracts bonding electrons equally towards themselves to form this sort of bond. It is more likely to happen in a molecule composed of same atoms. e.g. H2, N2 etc.
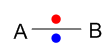
Here two equal electronegative atoms sharing electrons equally to form non polar covalent bond.
Polar Bond
When two atoms with a slight difference in electronegativities are bonded together, a polar bond is formed. The atom with more electronegativities attracts electron more than the other atom towards itself to form this type of bond. e.g. HCl, HF etc.
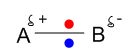
Here two atoms with a slight difference in electronegativity are sharing electrons unequally among themselves. As B is more electronegative than A, B attracts the bonding electrons towards itself to form polar bond.
Ionic bond
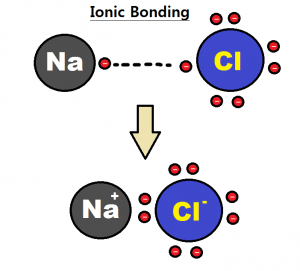
When two atoms with a greater difference in electronegativity bonded together, then ionic bond is formed. Here one electron is transferred from less electronegative atom to more electronegative atom to form this type of bond. e.g. NaCl.
Electronegativity in the periodic table
The Pauling scale is most commonly used to measure electronegativity. According to the scale Fluorine is the most electronegative element and its value is 4.0. Caesium and Francium are the least electronegative element and its value is 0.7.
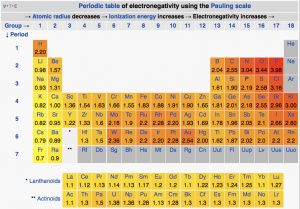
Here we can see that the electronegativity increases across the period and it decreases down the group. This can be explained with atomic number and the distance of valence electrons form nucleus.
Electronegativity increases across the period
Moving from left to right across a period, the number of protons and electrons increases while the number of energy shells stay same. Thus because of more attraction between increasing number of positive nucleus and negative electrons, the atomic radius decreases and the electronegativity (attraction of nucleus towards electrons) increases across the period.
Electronegativity decreases down the group
Moving down a group, the number of energy shells also increases with the increase of protons and electrons. So because of shielding effects of electrons in the increased inner shells, the attraction between electrons and nucleus (electronegativity) is reduced down the group.
Diagonal relationships in the periodic table
A diagonal relationship is said to exist between certain pairs of diagonally (not side by side) adjacent elements in second and third period in the periodic table.
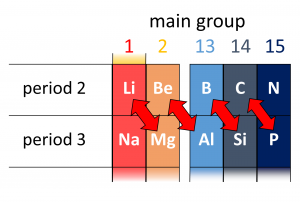
For example, lithium and magnesium, beryllium and aluminium, boron and silicon have similar properties. Boron and silicon both act as a semiconductors. This can be explained in terms of electronegativity.
We already have seen that electronegativity increases across the period in periodic table. So, for example, the electronegativity of boron is more than beryllium.
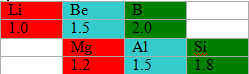
Again it decreases down the period, so the electronegativity of aluminium is less than boron. Thus berylium and aluminium both have less electronegativity than boron. This way the diagonal elements have similar (in this case same) electronegativities and similar properties than others.
Summary
- Electronegativity is the attractive force between the atom and the bonding electron pair.
- Non polar, polar and ionic bond is formed depending on the difference of electronegativity between two atoms.
- Electronegativity increases across the period in periodic table.
- Electronegativity decreases down the group in periodic table.
- Diagonal relationship observed between two elements in period 2 and 3 because of similarities in electronegativities.