- What is distillation:
Distillation is an ancient process which separates mixtures by using the relative boiling points of two substances. It is proved that the distillation process has been used by experimentalists from very earliest times. Aristotle explained the use of distillation form extraction of pure water by evaporating seas water [1]. As the distillation process is based on the difference in different physical properties as boiling points, vapour pressure and volatility, and then it is a physical process instead of chemical.
Two liquids having a boiling point difference of 25 degree Celsius or more are usually well separated by distillation. In case of substances which are non-volatile in nature, distillation is used to separate a liquid from that compound by using the property of viscosity.
The basic principle behind it is; heating a mixture till the boiling point of volatile compounds and vapors or gas produced by this process are collected back by condensation [2].
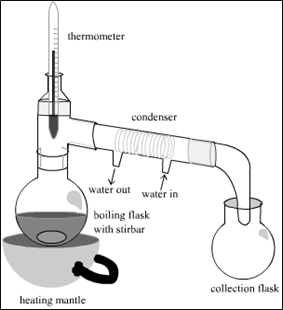
Fig 1: Simple distillation assembly consisting of these main parts
- What is steam distillation:
Steam distillation is used to distil compounds at a temperature lower than the normal boiling point. In this method, the desired material distilled at a temperature of fewer than 100 degrees [3].
Major conditions which are observed to use steam distillation are as follows:
- Extraction of temperature sensitive compounds
- When material to be extracted is immiscible
- When substance is chemically non reactive with water.
In this way it is possible to obtain a greater percentage of one of the two liquids in the condensate. We can repeat this operation time and time again to separate more and more liquid from the other one [4].
- Types of steam distillation:
Different modifications are made in steam distillation apparatus to get our desired results in separating different types of substances. Some of these modifications are discussed as under [5]:
- External steam distillation:
In External steam distillation, Steam is generated outside the tank in a steam generator or some boiler. The Sample to be extracted or separated is supported above the steam inlet. Standard apparatus used in external steam distillation is shown in figure 2.
As this modification in standard steam distillation procedure reduces time, thus it is recommended by various scientists [6] [7].
- Advantages and applications:
Main advantages of external steam distillation are:
- Steam intake can be controlled according to need of that procedure.
- Thermal decomposition can be avoided
- It is used majorly for oil production on industrial scale.
- Extraction of materials from body of plants such as roots and stem.
- It is used for distillation of high boiling oils
- Disadvantages:
- Highly expensive procedure
- Thermal decomposition can be avoided
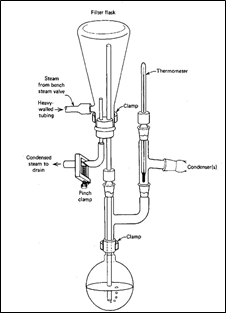
Figure 2: Apparatus for External steam distillation
- Internal steam distillation:
This is a relatively simple type of steam distillation and is used in various organic chemistry laboratories. In this method, substance to be separated and water is placed in a flask and thus steam source is present inside the apparatus. The standard apparatus used for internal steam distillation is explained in figure 3.
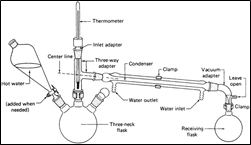
Figure 3: Internal steam distillation assembly
- Advantages and applications: By changing amount of water in distillation mixture, the water content in steam can be adjusted.Disadvantages:Difficult to handle due to complication of apparatusProlonged contact with water causes damage to material to be distilledPresence of water in end productTime consumingMicrowave assisted steam distillation
Microwave assisted steam distillation (MSD) is improved distillation technique which was produced to extract flavours from plant material. This method involves combination of steam distillation technique and microwave heating technique. This technique helps in initiation and further increasing in size of production of substance [8].
- Advantages and applications:
- Reduction in time of extraction.
- More powerful than standard steam distillation.
- Used for extraction of flavonoids.
- Better antioxidant activity attained in end product i.e. essential oil.
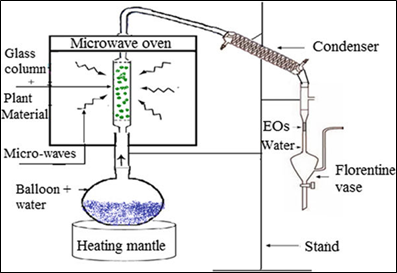
Figure 4: Microwave assisted steam distillation
- Water and steam distillation:
To avoid damage to the sample (to be distilled) by continuous intact with water, a new modification in steam distillation was made and it is called water and steam distillation. It involve the transfer of heat from steam to the material to be distilled and release of end product. After that, these prepared end product molecules are caught by vapor flow produced by water and as a result, a mixture of water and end product plus water is formed. These vapors are then shifted to the condenser to get the end product in pure form. [9]
- Advantages and applications: Maximum yield is obtained.
- Minimal loss of oxygenated components maximum yield as compared to water distillation
- Disadvantages: More time consuming due to due to the low pressure of rising steam. Water on the substance to be distilled causes it to vaporize in delayed time [10].
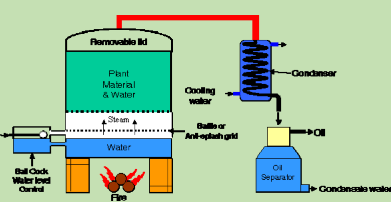
Figure 5: Water and Steam Distillation apparatus
- Principle of Steam Distillation:
In case of external steam distillation, Dry steam is passed out through material to be distilled (especially plants) and after that, the steam volatile compounds are volatized, condensed and collected [11].
In case of internal steam distillation, the water along with material to be distilled is boiled and the resultant vapours contain both water and the volatile component.
So, basic principle involves the interaction of steam with material to be distilled to push out volatile components from cells. Major example of using this procedure is to get essential oils from aromatic plants and certain useful nutrients from plants.
- Physiochemical Reactions involved:
Three major physiochemical processes involved in almost all steam distillations procedures. These processes define the advantages and disadvantages of this very procedure. Taking example of plant cells having essential oils are as follows:
- Diffusion:
Steam once comes near plant cells, triggers the process of osmosis within the plant cell. This starts when, the system achieves temperature equal to the boiling point of water, a part of volatile oil dissolves in the water present within the glands containing essential oils, and this oil-water solution permeates, by osmosis, the swollen membranes and finally reaches the outer surface, where the oil is vaporized by passing steam. For better production following this process, it is necessary to thorough mix substance to be distilled with water before starting the procedure.
- Hydrolysis:
After Diffusion, the process of hydrolysis is started. In this context, hydrolysis means the reaction of water with certain constituents of essential oils. For example, Esters in the presence of water at high temperatures tend to react with water to form acids and alcohols. This by-product reduces the yield of the desired compound i.e. essential oil.
This leads to the major drawback of steam distillation as by increasing amount to water, the amount of by-products production is also increased which reduces the yield and increases the processing time. This problem can be solved by using a lower amount of water as possible.
- Decomposition by heat:
Almost all components of essential oils are unstable at higher temperatures, so to avoid decomposition by heat, the distillation should be performed at lower temperatures and this lower temperature should be maintained.
- Applications of steam distillation:
Steam distillation procedures are used in various industrial procedures which are discussed as under: [12]
- Extraction of essential oils:
Essential oils are highly volatile substances isolated by different physical processes from an odoriferous plant of a single botanical species. The oil bears the name of the plant from which it is derived; for example, Rose oil or peppermint oil. Such oils were called essential because they were thought to represent the very essence of odor and flavor. Different methods of steam distillations are used for this purpose at a small scale level as well at the industrial level [13].
- Separation of fatty acids from mixtures:
Steam distillations used for purification of fatty acids from last many years. It is also used for determination of a certain amount of fatty acids in a compound.
- Checking quality of food materials:
Steam distillations used in various industrial processes to check quality and impurity level in certain foods.
- Juice analysis:
Amount of volatile acids in certain juices and wines is estimated by using steam distillation [14].
- Petroleum refineries:
Crude oil contains various components and each component is isolated stepwise in oil refineries. This is done by using steam distillation procedures. [15]
- Flavour extraction:
A partial modification technique of Steam-distillation has been used for the isolation of dairy flavours from dairy products.
- Conclusion:
Steam distillation is the most widely used method for the extraction of essential oils and isolation of petroleum components. Proper selection of the distillation technique, play a vital role in determining the quality and yield of end products. Various modifications in this technique are helping scientists in getting better yield and good quality product in lesser time.
References:
- https://www.britannica.com/science/distillation#ref27766
- https://sciencing.com/steam-distillation-vs-simple-distillation-8407975.html
- Hand book of laboratory distillation with an introduction to pilot plant distillation”. By Erih Krell
- https://www.gadoi.it/en/steam-distillation/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/hydrodistillation/pdf
- Handa, S.S. & Khanuja, Suman & Longo, G. & Rakesh, D.D.. (2008). Extraction technologies for medicinal and aromatic plants. International centre for science and high technology. 21-25.
- Azmir Sahraoui, Naima & Vian, Maryline & Bornard, Isabelle & Boutekedjiret, Chahrazed & Chemat, Farid. (2008). Improved microwave steam distillation apparatus for isolation of essential oils. Comparison with conventional steam distillation. Journal of chromatography. A. 1210. 229-33. 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.09.078.
- https://www.gadoi.it/en/steam-distillation/
- Talati, Ali. (2017). Extraction methods of natural essential oils. 10.13140/rg.2.2.18744.34564.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/hydrodistillation/pdf
- Handbook of Herbs and Spices Volume 1 , A volume in Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition Book • 2012 Edited by: K.V. Peter
- https://www.britannica.com/topic/essential-oil/Chemical-composition
- https://www.buchi.com/en/content/determination-volatile-acids-wine-and-juice
- https://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/energy/oil-refining4.htm
- M. Sibeijn, J.A. Wouters, 18 – Production of dairy aromas and flavors: New directions, Editor(s): Milena Corredig, In Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition, Dairy-Derived Ingredients, Woodhead Publishing, 2009, Pages 470-481, ISBN 9781845694654, https://doi.org/10.1533/9781845697198.3.47