Chlorine
Explanation
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and it has atomic number 17. Chlorine is the second member of halogen group it has similar properties like fluorine, bromine and iodine. Chlorine has electronic configuration [Ne] 3s23p5 with the seven electrons in the third outermost shell acting as its valence electrons.
Chlorine has two stable isotopes: chlorine – 35 and chorine – 37. The atomic weight of chlorine given on the periodic table is 35.47 u. Different isotopes have different relative abundances ,chlorine – 35 has a relative abundance of 75.76% ,whereas chlorine – 37 has a relative abundance of 24.24%. Chlorine -35 is about 3 times more abundant than chlorine – 37, the weighted average is closer to 35 than 37.
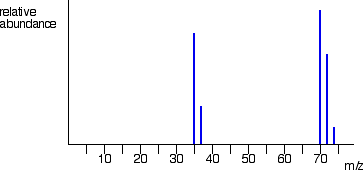
The mass spectrum of Chlorine
Chlorine is such an element which contain more than one atom per molecule. It has two isotopes Cl-35 and Cl-37, so it contain 3 atoms of Cl-35 and 1 atom of Cl-37. It consist of molecules so when it passed into the ionization chamber, the electrons are knocked off, and give molecular ion, Cl2+. The ions are not stable so some will form chlorine atom and a Cl+ ion. This process is called fragmentation.
Cl2+ → Cl + Cl+
The Cl atom is neither accelerated nor deflected in the machine it is not ionized in the ionization chamber and simply lost. But Cl+ ions will pass through the machine and give lines at 35 and 37 it is depend upon isotopes.
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an important method which is used to identify elements and compounds by their mass spectrum. Mass spectrometry is a technique used to determine relative isotopic masses of different elements and relative abundance of the isotopes.
In all types of mass spectroscopy they include vaporing atoms or molecules in high vacuum and create electron bombardment to generate a beam of positive ions called ionization. Mass spectrometer separates and counts the numbers of different positive ions particles are released, the resulting product from the detector is known as mass spectrum (plural mass spectra).
These are different types of mass spectrometer:
Method No. 1. Deflection Mass Spectrometer:
It is also called as TOF type. Deflection mass spectrometer consists of ionization, acceleration the positive ions, which in turn deflection of ions and ion detection followed by deflection, separation and detection. The substance which is to be analyzed is injected in the high vacuum tube system which has extremely low pressure particles are ionized through colliding with beam of high speed electron.
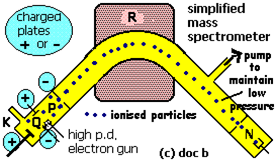
In the above diagram the symbol K as sample and Q as high voltage supply label. High voltage electron gun falls a beam of high energy electrons from a heated metal element into the vaporized sample under analysis and causes ionization of the atoms or molecule form positive ions. The collision of high energy electrons with atoms or molecules causes another electron to remove the particle as positively charged particle. The sample must in the gaseous phase, In case of chlorine:
Cl (g) + e– = Cl + (g) + e–
The low pressure vacuum is needed to stop the ions to collide with air particles which affect the motion of particles to reach the ion detector system.
Negative plate as P in above diagram. Negative plates accelerate the positive ions to move through the tube. The moving charge particles create a magnetic field around itself which interact with magnetic field of the system at point R [2].
Deflection of ions due to magnetic field is label as R. Magnetic field deflect the mono-positive ions according to their increasing mass towards the ion detection system. All like mass particles move down the tube. Ion detection system is labelled as N. ions strike the ion detection system where they generate a small electrical current. This small current convert into electronic signals appear as ion peaks which sent to computer for analysis and display as mass spectrum. The data is displayed as m/z versus peak height. m/z means relative mass over charge which help to know relative atomic mass of ionized particle.
| Ion | Relative mass (m) | Positive ion charge (z) | m/z ratio |
| [35Cl]+ | 37 | 1 | 35/1 = 35 |
| [35Cl2]+ | 70 | 1 | 70/1 = 70 |
| [35Cl2]2+ | 70 | 2 | 70/2 = 35 |
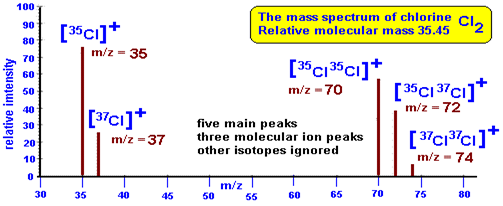
The mass spectrum of chlorine is good example of molecular element. Chlorine has two stable isotopes; chlorine-37 (25%) and chlorine -35 (75%).There are five main peaks of isotopes of chlorine of various isotopic monatomic ions.
- [37 Cl2]+ m\z = 74 ( molecular ion)
- [37 Cl 35 Cl]+ m\z = 72
- [35 Cl2]+ m/z= 70 (molecular ion)
- [37 Cl]+ m/z = 37 (monatomic ion)
- [35 Cl]+ m/z = 35 (monoatomic ion)
The presence of five peaks for chlorine shows the ratio of heights for peaks 1 and 2 is 3: 1. For bimolecular ions, ¾ of the chlorine isotopes are Cl 35 and ¼ of the isotope of chlorine is cl37.
The mass spectrum of an organic compound having chlorine atoms also show different mass spectrum. Organic compound having one chlorine atom show molecular peaks M+ and M+2.the molecular ion containing 35Cl isotope has relative atomic mass 78 whereas molecular ion containing 37Cl has relative atomic mass 80.
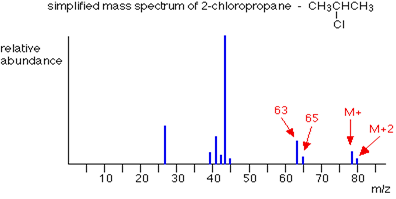
Mass spectrum of 2-chloropropane is given below. In this mass spectrum the peak heights of chlorine are in the ratio of 3:1 which show that lighter isotope of chlorine is attached with more number of molecules as compared to the heavier isotope. The fragmentation of 2-chloropropane formed are
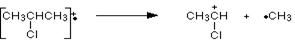
Same pattern of peaks are observed at m/z = 63 and m/z = 65 due to chlorine atoms which is attached to CH3CH forming positive ion.
The organic compound having two chlorine atoms show three peaks due different combinations of isotopes of chlorine are attached with carbon and hydrogen. The ratio observed in this case is 9:6:1.the compound containing 2 chlorine atom have difference in ratio due to isotopes attached with fragments.
Method No. 2. Time of Flight (TOF) Mass Spectrometer
The principle of this method is also include ionization, acceleration to donate constant kinetic energy to all ions, ions drift, ions detection and also data analysis, all things are controlled and carried out with the help of computers now a days.
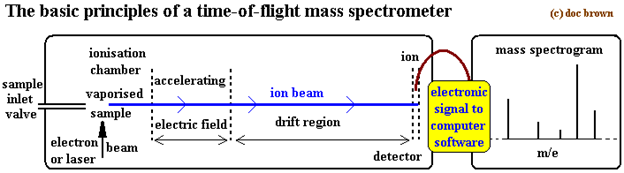
The ions are formed similarly through electron bombardment and the ions which are produced as a result of bombardment are accelerated between electrically charged plates. The sample must be in gaseous form, laser beam is used to accelerate electrons and produced positive ions. In this process magnetic field is not used to separate the positive ions.
In this process the ionized particle which has smaller mass has smaller time of flight in the drift region so in this case ions are separate on the base of their time of flight.
t=Kinst √(m/q)
t=time of flight
m=mass of ion
q=charge on ion
√=square root of
Kinst = a proportionality constant based on the instrument settings and characteristics e.g. the electric field strength, length of analyzing tube etc.
References:
- https://www.chemguide.co.uk/analysis/masspec/elements.html
- http://www.docbrown.info/page04/4_71atomMSintro.htm