Definition of carboxylic acid
Organic compounds containing carboxyl functional group (-COOH) are called carboxylic acid. The general formula of carboxylic acid is:
Carboxylic acid is composed of two functional groups carbonyl group (-CO-) and hydroxyl group(-OH). The name carboxyl derived from the first four letters of carbonyl and the last four letters of hydroxyl.
Classification
Depending on the number of carboxylic acid group present, it is classified as monocarboxylic acid, dicarboxylic acid, tricarboxylic acid or tetracarboxylic acid. An example of tetracarboxylic acid is given below:
Nomenclature
In IUPAC system the carboxylic acid is named as alkanoic acid. The suffix in alkane -e is replaced by -oic acid to give the name of the corresponding carboxylic acid. For example:
HCOOH Methanoic acid
CH2COOH Ethanoic acid
CH2CH2COOH Propanoic acid
The compounds contain branch or substituents in different position, the longest carbon chain with carboxylic acid is selected and numbered started from the carbon contains carboxyl functional group (-COOH).
For the small chain acids, common names are mostly used. There are no rules for these but end with -ic acid. For example:
HCOOH Formic acid
CH2COOH Acetic acid
Physical properties
Boiling point
The boiling point of carboxylic acid increases with the increase of molecular weight. Boiling point of carboxylic acid is higher than the boiling point of alcohols with same or similar molecular weight. This is because of the formation of dimer between two acids by hydrogen bonding. Before the acid boils the hydrogen bonds in the dimer must be broken, thus the boiling point rises up.

Solubility
Lower chain carboxylic acids are soluble in water but higher chain carboxylic acids are insoluble. Carboxylic acid is polar compound. It has both hydrogen bond acceptor (the carbonyl -C=O oxygen) and hydrogen bond donor (the hydrogen in -COOH group). Thus they form hydrogen bond with water to become water soluble. But because of the hydrophobic nature of the aliphatic chain as the carbon chain increases, the solubility in decreases. For the same reason the higher chain acids are readily soluble in non polar or less polar solvent like ethanol, ether and benzene.
Acidity
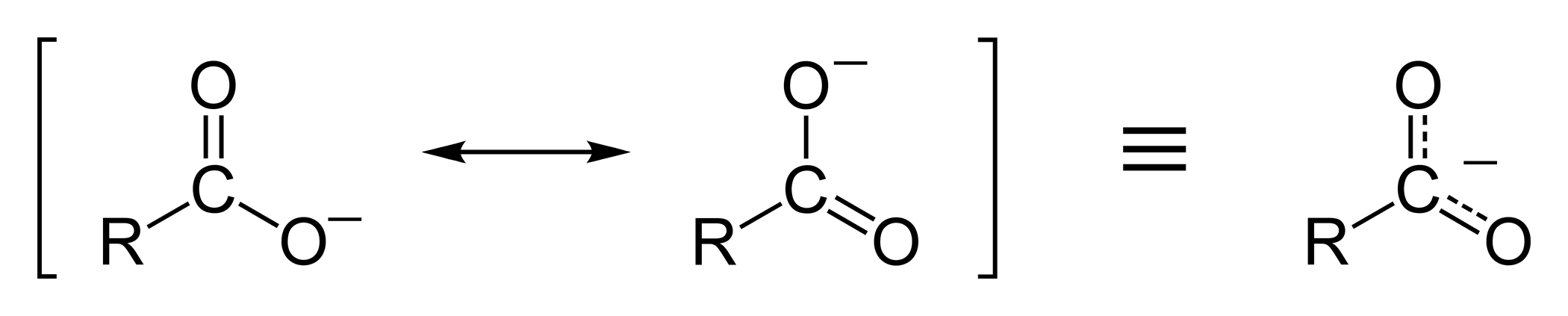
In aqueous solution, Carboxylic acid dissociates to give H+ cations and RCOO– anions. The negative charge on carboxylate anion is delocalized over the two oxygen and carbon atom. Thus it acts as a weak acid.
Preparation
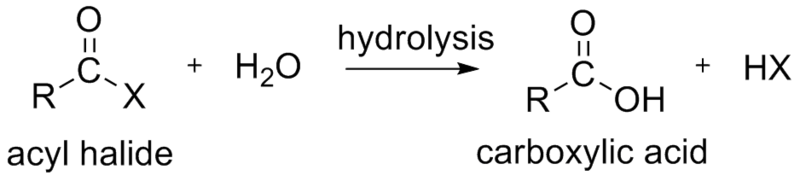
- Carboxylic acid can be prepared by the hydrolysis with acyl halide.
- Oxidation of primary alcohols produce carboxylic acid. Potassium dichromate or potassium permanganate can be used as a oxidizing agent.

Reactions
- Carboxylic acid reacts with base to form carboxylate ion, carbon dioxide and water. Here the acidic hydrogen is replaced by a metal ion.
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COO−Na+ + CO2 + H2O
- Carboxylic acid reacts with thionyl chloride to form acyl chloride. Here the electron rich C=O attacks the electron deficient sulphur in thionyl chloride.
- The reduction of carboxylic acid with LiAlH4 in ether gives corresponding alcohol.
- Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol to form ester. This is a very useful reaction to produce polyester in factory. Two carboxylic acid react to form acid anhydride. Carboxylic acid can also produce amide. This is a stepwise reaction via the production of ester. This is a very important reaction as it is used in the production of peptides. The following diagram shows that ester, acid anhydride, amide and acyl chloride can be formed from carboxylic acid.
![Carboxylic acid 25 By Vladislav Andriashvili (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e2/Carboxylic_Acid_Sunshine_Diagram.jpg)
Summary
- Organic compounds containing carboxyl functional group (-COOH) are called carboxylic acid.
- In IUPAC system the carboxylic acid is named as alkanoic acid.
- The boiling point of carboxylic acid increases with the increase of molecular weight.
- Boiling point of carboxylic acid is higher than the boiling point of alcohols with same or similar molecular weight.
- Lower chain carboxylic acids are soluble in water but higher chain carboxylic acids are insoluble.
- It acts as a weak acid.
![Carboxylic acid 23 By Rifleman 82 (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b0/Action_of_thionyl_chloride_on_carboxylic_acid.png)
![Carboxylic acid 24 By Pete Davis (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/cf/Alcohols_from_carboxylic_acid_via_reduction.png)